Understanding Piraminds: Origins and Significance
The fascination with the piraminds extends beyond their monumental structures; they represent ancient civilizations’ engineering prowess and cultural significance. Predominantly associated with ancient Egypt, piraminds are architectural marvels that have captured human imagination for centuries.
Historical Context of Piraminds
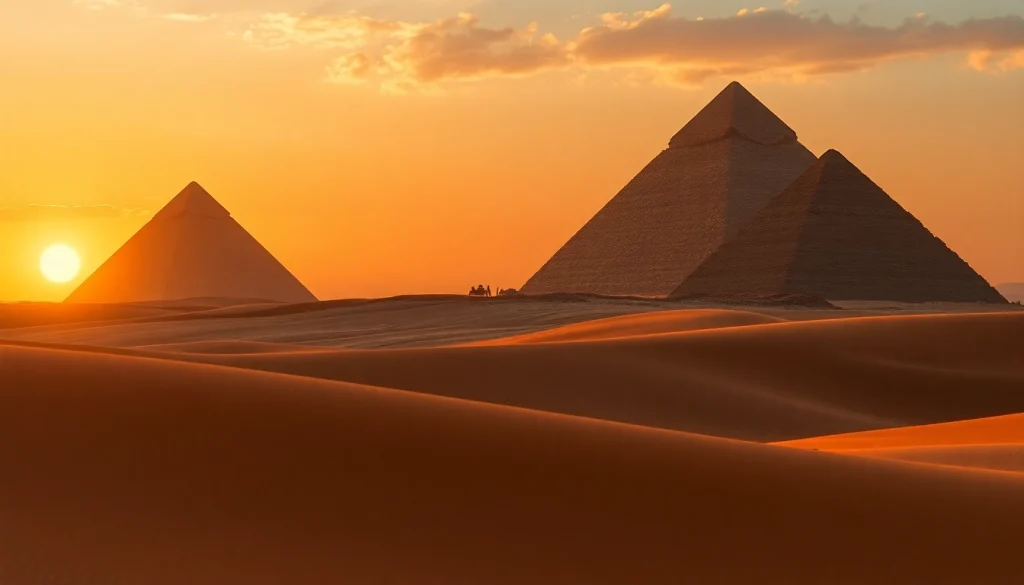
The term “piraminds” primarily conjures images of the pyramids of Egypt, especially the iconic Great Pyramid of Giza. These structures were built during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods as monumental tombs for pharaohs and their consorts. The construction began around 2670 BCE, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ belief in an afterlife, where the pyramid served as a means for the pharaoh to ascend to the heavens.
Piraminds are not a uniquely Egyptian phenomenon; similar structures have been found in various cultures, including the Mesoamerican civilizations, such as the Mayans and Aztecs, who built step pyramids for ceremonial purposes. Each culture’s piramid designs were emblematic of their theological beliefs and societal structures, reinforcing their significance as architectural icons across civilizations.
Architecture and Engineering Marvels
Standing as colossal structures, piraminds boast sophisticated construction methods that have intrigued historians and archaeologists alike. The Great Pyramid, for instance, originally stood at approximately 146.6 meters (481 feet), and was the tallest man-made structure in the world for 3,800 years. Its base covers over 13 acres, demonstrating the advanced planning and engineering skills possessed by ancient Egyptians.
The alignment of pyramids with celestial bodies such as the North Star suggests advanced astronomical knowledge. The use of vast quantities of limestone, granite, and basalt—sourced from nearby quarries—illustrates the logistical prowess required to construct these buildings. These structures’ durability, having endured millennia, speaks volumes about ancient construction techniques and the resources they harnessed.
Cultural Importance in Ancient Civilizations
Piraminds symbolized not only the immense power of rulers but also served as a testament to the religious beliefs prevalent in ancient societies. In Egypt, the pyramids were seen as gateways to the afterlife and were laden with rich symbolism, linking the pharaoh’s divine status with his journey beyond death.
The significance of these structures is also reflected in burial practices, as they housed the pharaoh’s tombs and treasures needed for the afterlife. Likewise, piraminds in Mesoamerica served both as tombs and temples, integrating spiritual practices with socio-political themes, underlining their multifaceted purpose in ancient cultures.
The Construction Techniques Behind Piraminds
Materials Used in Building Piraminds
The construction of piraminds relied on local materials that were strategically chosen based on availability and structural properties. In ancient Egypt, limestone, granite, and sandstone were predominant materials. The outer casing stones of the Great Pyramid, polished Tura limestone, were especially prized for their aesthetic properties, reflecting sunlight and creating a stunning effect.
In contrast, Mesoamerican piraminds often incorporated adobe bricks and volcanic stones, showcasing their adaptive strategies in utilizing local resources. The choice of materials was crucial for ensuring the longevity and stability of these structures, allowing them to survive through centuries of environmental exposure.
Labor and Workforce Dynamics
The creation of piraminds was a monumental undertaking involving vast labor forces. Contrary to popular belief that enslaved individuals built the pyramids, evidence suggests that skilled laborers, craftsmen, and seasonal workers played pivotal roles. These workers were often organized in teams and housed in nearby settlements, demonstrating a level of social structure and organization.
Records indicate that during the construction of the Great Pyramid, approximately 20,000 to 30,000 workers participated. These individuals were likely motivated by a mixture of civic pride, religious duty, and economic opportunity, challenging the stereotypes about the labor force during ancient times.
Innovations in Construction Methodologies
The construction methodologies employed in building piraminds have been the subject of extensive study and debate. Innovations such as the use of ramps, levers, and sledges enabled workers to transport massive stones from quarries to construction sites effectively. Various ramp theories—including straight, zigzag, and circular—are explored by archaeologists to unravel the exact methods used.
Additionally, developments in tools, such as copper chisels and stone hammers, facilitated the precise shaping of stones. The collaborative efforts of architects, laborers, and artisans reflect an ancient understanding of engineering principles that were critical for these architectural feats.
Exploring Famous Piraminds Around the World
Giza and its Iconic Structures
The Giza pyramid complex, comprising the Great Pyramid, Khafre, and Menkaure, stands as a pinnacle of ancient engineering and architecture. The Great Pyramid alone is a UNESCO World Heritage site and serves as a symbol of Egypt’s rich history. Each of these pyramids is emblematic of the corresponding pharaoh’s reign and reflects distinct architectural styles and techniques.
The Sphinx, adjacent to the pyramids, further enhances Giza’s status as a center of ancient civilization. This enigmatic structure, often believed to guard the pyramids, presents a blend of human and lion symbolism, showcasing the spiritual and cultural narratives of the time.
The Lesser Known Piraminds
While the Giza pyramids are widely recognized, numerous lesser-known piraminds exist globally. The Nubian pyramids in modern-day Sudan, for example, represent the Kingdom of Kush’s grandeur, with over 200 pyramids built as royal tombs. These structures, smaller yet profound in significance, reflect a rich history of dynasties that ruled Africa.
In Mesoamerica, the Pyramid of the Sun and the Pyramid of the Moon at Teotihuacan offer insights into pre-Columbian civilizations. The construction of step pyramids, embellished with temples, highlights the amalgamation of spiritual, political, and astronomical elements, cementing their importance in understanding ancient indigenous cultures.
Piraminds in Popular Culture
The intrigue surrounding piraminds extends into popular culture, where they have appeared in various films, documentaries, and literature. These cultural references not only seek to entertain but often serve to educate audiences about ancient civilizations and their monumental achievements.
From movies like “The Mummy” to documentaries exploring the mysteries of piraminds, these representations play an essential role in sustaining public interest and invoking curiosity about humanity’s past. The enduring fascination with piraminds as symbols of mystery and awe signifies their impact across generations.
Modern-Day Archaeological Discoveries
Recent Findings Related to Piraminds
Recent archaeological endeavors have rekindled interest in piraminds, yielding significant discoveries that enhance our understanding of these ancient structures. Technologies such as ground-penetrating radar have uncovered hidden features beneath the Giza pyramids, indicating potential chambers and structural innovations previously unknown.
Such findings underscore the notion that much about piraminds remains to be discovered, further emphasizing the importance of ongoing archaeological research and excavation efforts to unveil secrets long buried under centuries of sediment and sand.
Technological Advancements in Archaeology
The advent of technology has revolutionized the field of archaeology, enabling researchers to explore and understand piraminds with greater precision. Techniques like 3D scanning, photogrammetry, and drone surveys allow for the documentation of sites without intrusive excavation.
Moreover, these technological tools facilitate better preservation strategies and provide new insights into construction techniques and cultural practices. By combining traditional archaeological methods with modern technology, researchers continue to construct a more comprehensive picture of past civilizations.
Preservation Efforts for Piraminds
Preserving piraminds is crucial due to their historical and cultural significance. Various initiatives and organizations work diligently to restore and maintain these structures against the impacts of erosion, pollution, and tourism. Programs aimed at conservation emphasize sustainable tourism practices to ensure that future generations can continue to appreciate these monumental legacies.
Collaboration between governments, archaeologists, and local communities plays an essential role in implementing effective preservation strategies, protecting these symbols of human achievement for years to come.
FAQs About Piraminds
What are piraminds made of?
Piraminds are primarily constructed from limestone, granite, and other locally sourced materials, depending on the region and available resources.
How were piraminds built?
Ancient Egyptians built piraminds using manpower, basic tools, and innovative techniques that involved transporting large stone blocks, often utilizing ramps.
What is the purpose of piraminds?
Piraminds served as monumental tombs for pharaohs and high-ranking officials, symbolizing their journey to the afterlife and connection to the divine.
Are there piraminds outside Egypt?
Yes, piraminds can be found in regions like Mexico, Sudan, and Cambodia, each representing unique cultural and historical significance.
How can I visit famous piraminds?
Visitors can tour famous piraminds through organized travel agencies or by visiting historical sites directly, enjoying guided experiences that explore their rich histories.